About India
About India
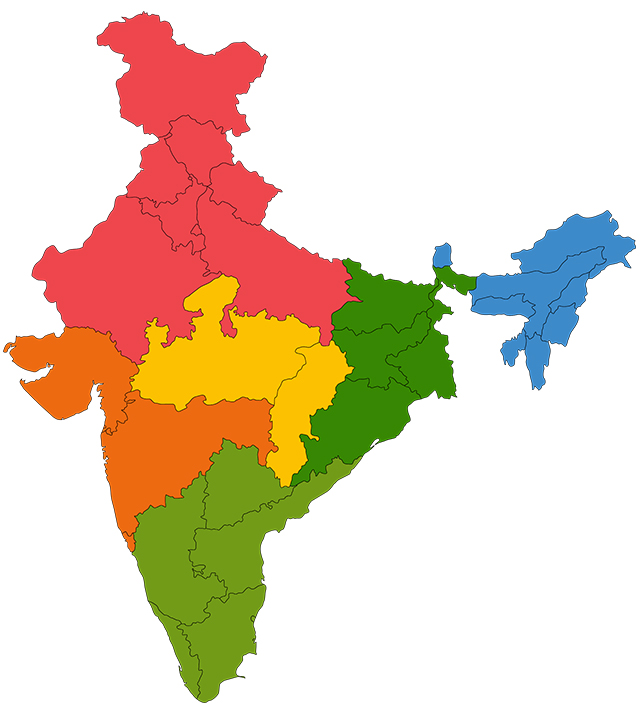
India has always been there melting pot culture. India, the delta of Asia is an amalgamation of Asia's culture, history, heritage and food. Known as the second most populated country of the world but that has never held it back from identifying itself as an example of multi-cultural, multi-lingual, secular state which has made its mark in the world map. With a past dating back to 2000 BC to a very sophisticated urbanized culture of Indus Valley civilization India has been self-sufficient throughout history, giving rise to (Sikhism, Buddhism and Jainism), refuge to (Judaism and Zoroastrianism) and adapting (Christianity and Islam) many religions while maintaining its strong roots in Hinduism. India’s vibrant history begins with the Vedic period in the ancient times, to incursions from the north and the north western region during the medieval period and its long past of colonization in the modern period. India’s diverse culture can be found in its every small nooks and corner which tells a story of its long past and its shinning future. All of its 29 states has it own history language heritage culture and food habits based on its geography flora and fauna. With Himalayas in the north, Thar Desert in the west, Deccan plateau in the south and the delta of Sundarbans in the east and three oceans giving it a long coastline, India has developed its unique flora and fauna which has continuously contributed to the enriching lifestyle of India. Each part of India has its own character which comes from its landscape with its own language, culture and food habits. The Northern part of India with Himalayas as its boundary is the birth place of the main rivers and gives protection from the cold Siberian winds. In spite of the Himalayas North has also been subjected to a large number of invasions from the Arabs, Turks and the Persians thus, the culture and history of this region is a perfect blend of various ethnic groups of central Asia and middle-east.
Within India the Himalayas are divided into three longitudinal belts, called the Outer, Lesser, and Great Himalayas. At each extremity there is a great bend in the system’s alignment, from which a number of lower mountain ranges and hills spread out. The outer range of Himalayas, The Shivalik range which cover the area of West Bengal, Duars spreading to the north east is home to a diverse biodiversity which gives rise to a distinctive culture and history completely different from the rest of India. The fertile plains of the Northern basin of the river Ganga is called as the granary of the subcontinent. The Ganges basin covers the states of Uttar Pradesh Bihar along with its delta in west Bengal which is the delta basin for the river Brahmaputra, Ganga and Yamuna. The Great Indian, or Thar, Desert forms an important southern extension of the Indo-Gangetic Plain. It is mostly in northwestern India but also extends into eastern Pakistan and is mainly an area of gently undulating terrain, and within it are several areas dominated by shifting sand dunes and numerous isolated hills.
The Deccan plateau is the region between the oceans Bay of Bengal and Arabian Sea and is separated from the north with Vindhya Range. Being part of the Gondowana land this part of India is part of the oldest landmass of the world and is the most geologically stable part of India. The Deccan has developed a culture and heritage which has its traces in the Indus Valley civilization. It is so believed the genealogically there traces of people belonging to the Indus Valley Civilization. The Western Ghats rises abruptly on the western side of the Deccan plateau separating it from the Arabian Sea. This gives rise to an exceptional coastline and which is has been the entry point for many Europeans leading up to the colonization of India. The states which cover the Western Ghats are Maharashtra Kerala parts of Gujarat and Karnataka. The Eastern Ghats by the Bay of Bengal is home to the ancient most mountain range of the country covering parts of Andhra Pradesh and Orissa. It is also the place where we find range of ancient temples and numerous rivers. It is also the area of the great ruler Ashoka and the area of the Great War of Kalinga. The coastal region in the west starts from the salt valleys of Runn of Katch the union territories of Daman and Diu, the beaches of Goa and the back waters of the Kerala and the fertile delta region of the eastern coast. The life history, culture food and livelihood of these places depend highly on the ocean. Apart from the prominent Mughal history of the north the Deccan also has its contribution to the history of India which also included naval expeditions to the south east of Asia and spreading the culture and heritage of Indi. The major dynasties of indian Deccan history includes Pallavas, Chalukyas, Rashtrakuta, the Vijaynagar empire, the Marathas the Nizam’s of Hyderabad and the Muslim bahamani Sultunate of Deccan.
Contemporary India’s increasing physical prosperity and cultural dynamism—despite continued domestic challenges and economic inequality—are seen in its well-developed infrastructure and a highly diversified industrial base, in its pool of scientific and engineering personnel (one of the largest in the world), in the pace of its agricultural expansion, and in its rich and vibrant cultural exports of music, literature, and cinema. Though the country’s population is largely rural, India has the most populated cosmopolitan cities of the world – Kolkata, Mumbai, Delhi and Bangalore.







